Abstract
Background
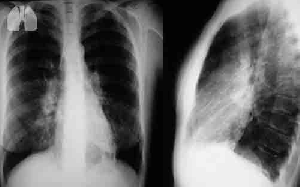
The prevalence of lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains elusive. Therefore, we set up a multicentric prospective study to investigate the presence of interstitial lung disease (ILD), emphysema, bronchiolitis and nodules in early RA.
Methods
We recruited patients with RA and a disease duration from 1 to 10?years to screening. Patients underwent comprehensive respiratory evaluation consisting of an environmental questionnaire, HRCT, pulmonary function tests (PFT) and sampling for genetic analysis of common variants associated with RA-ILD. HRCT were centrally reviewed.
Results
We included 258 RA patients, median age 56?years old, 71% female, 49% ex- or current smokers. We detected ILD, emphysema and >20% air trapping in 38 (15%), 51 (20%) and 89 (34%) patients, respectively. Older age, male gender, disease activity and lower diffusion capacity (DLCO) were significantly associated with ILD; older age, male gender, smoking status and lower DLCO were associated with emphysema. No variables were associated with air trapping. Finally, we built stepwise logistic regression models for ILD and emphysema. Older age, higher DAS-28, seropositivity for rheumatoid factor, lower DLCO and MUC5B variant were predictors of ILD while the number of pack-years smoking was predictive of emphysema.
Conclusions
Lung involvement affects a high proportion of early-stage RA patients, constrictive bronchiolitis being the most prevalent, followed by emphysema and ILD. Older age, uncontrolled disease, male gender and lower DLCO were associated with both ILD and emphysema, suggesting that we should prioritise screening in these subpopulations.