Abstract
Background
Respiratory oscillometry measures the physiological effort and mechanics of moving air in and out of the lungs during normal breathing. It provides complementary information to spirometry. Uncertainty regarding the interpretation of oscillometry is a barrier to routine use.
The aim of this study was to aid the interpretation of oscillometry amongst adult patients with asthma or COPD by generating expert consensus statements.
Methods
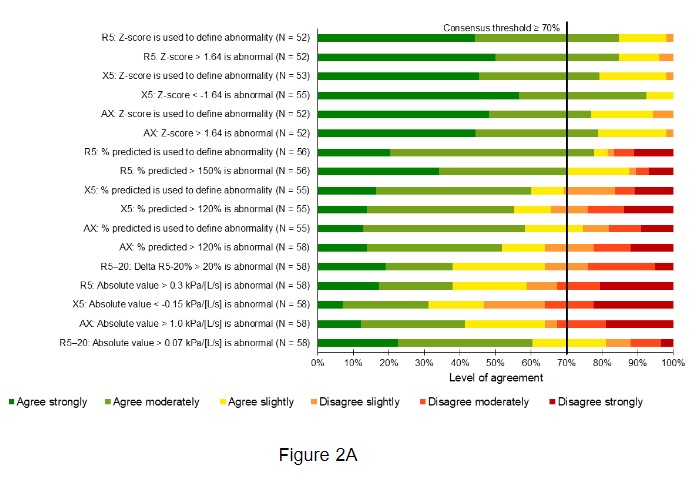
A Delphi method was used to develop consensus statements regarding the clinical use of oscillometry in adults to identify abnormal lung function, bronchodilator response (BDR) and minimal clinically important differences (MCID). Initial statements were refined in the brainstorming round. Statements were assessed by 60 pulmonologists over three rounds, with consensus defined as ≥70% agreement.
Results
Pulmonologists agreed that oscillometry is clinically useful to assess abnormal lung function, its severity, and measure BDR. High consensus was reached for resistance (R5, 85%), reactance (X5, 79%) and area under the reactance curve (AX, 77%) based on Z-scores, where >1.64 was considered abnormal for R5 and AX and >−1.64 considered abnormal for X5. For measuring BDR, good agreement was based on the use of percentage change for R5, X5 and AX.
Discussion
This international Delphi study combine evidence based and expert opinion to inform clinicians in the interpretation of respiratory oscillometry. Focusing on a few key parameters of oscillometry will allow clinicians to become confident in its everyday use to assess abnormal lung function, grade the severity of impairment, monitor progression over time, and assess BDR.